×
×
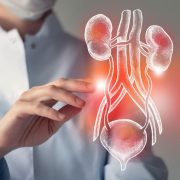
Select a Test
Select Date & Time
Please select a date !
Enter Personal Information
Payment Option
Insurance & Payment
Insurance & Payment
Confirm & Submit
✔ Review your appointment details before submitting.
❗ You will receive a confirmation email after booking.
Thank You for Booking!
×Your test appointment has been successfully registered, Please check you email for details.
 ×
×
Select a Test
Select Date & Time
Please select a date !
Enter Personal Information
Payment Option
Insurance & Payment
Insurance & Payment
Confirm & Submit
✔ Review your appointment details before submitting.
❗ You will receive a confirmation email after booking.
Thank You for Booking!
×Your test appointment has been successfully registered, Please check you email for details.